food poisoning- one of the most common types of intoxication of the body. Every year, about two million deaths are recorded in the world for this reason. Therefore, everyone needs to know what signs are observed when food is poisoned, and how to provide first aid.
Food poisoning refers to conditions resulting from the consumption of spoiled or toxic food. Intoxication is caused by pathogenic microorganisms or the action of a toxic compound that enters the body with food.
Features of food poisoning
Food poisoning always manifests itself quickly, the symptoms are growing rapidly. Depending on the type of toxin and its volume depends on the intensity and speed of symptoms. It also matters whether an adult or a child has been poisoned.
On average, such intoxications appear in the period from half an hour to three or four hours.
A feature of food poisoning is always a clearly identified relationship between the use of any product and the development of a disease state. If the whole family is poisoned by soup, then signs of poisoning by this food will appear in everyone without exception. In addition, food intoxications are characterized by the fact that they are not contagious, even if they are caused by infectious agents.
Types of food poisoning
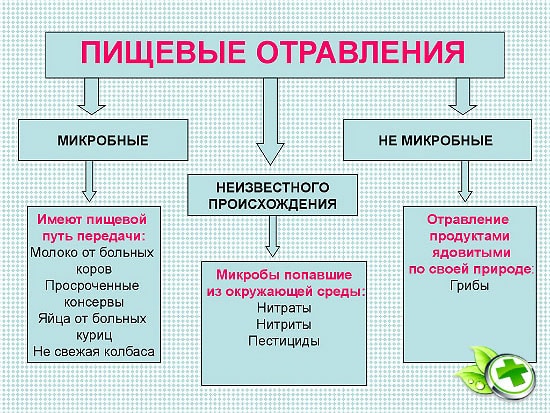
Depending on the type of toxin, poisoning is divided into infectious and non-infectious. Toxic infections are caused by various types of pathogenic microflora, the most dangerous of which are botulism and staphylococcus aureus.
Quite often there are intoxications provoked by mold fungi. Toxoinfection is the result of the action not only of the microorganisms themselves, but also of their waste products.
Occur as a result of eating naturally poisonous species of plants, fish and animals (for example, fugu or fly agaric) or spoiled products that become toxic if not stored correctly or expired.
In addition, the cause of intoxication can be food that has been contaminated with poisons due to a violation of the cultivation, production or packaging technology. Poisoning with fatty foods is also possible, observed with excessive consumption of fats, especially animals, and simple carbohydrates.
First manifestations

Symptoms of any food poisoning appear fairly quickly. Since the penetration of the poisoned product occurs through the organs of the digestive tract, it is the first to react to intoxication. The first manifestations of food intoxication are vomiting, severe abdominal pain, diarrhea.
If poisoning with fatty foods has occurred, then there will be symptoms such as increased gas formation, a feeling of severe heaviness in the abdomen.
When toxic substances begin to penetrate into the bloodstream through the walls of the stomach, general malaise, lethargy, and fever appear. There may be pain and aches in the muscles and joints, fever. In acute intoxications, accompanied by profuse vomiting, large losses of water are always noted.
If they are not replenished, the body is threatened with dehydration, which is the main cause of death. If a small child has been poisoned, who cannot communicate in words about his condition, then it is necessary to carefully monitor him. Dehydration is manifested by excessive dryness of the mucous membranes, intense thirst, lack of urination, shortness of breath, and rapid heartbeat.
Most cases of food intoxication can be cured on their own, without the involvement of doctors, and pass within a few days.
If profuse vomiting and diarrhea do not stop for a day or more, a high temperature resistant to medicines persists, it is necessary to seek qualified medical help.
Signs of severe poisoning
With severe intoxication, all the same manifestations are observed, but they are of greater intensity, appear sharply and very quickly. If a strong toxic compound has entered the body or a person has consumed a large amount of toxin, there are signs of damage to the nervous system.
These are various disorders of the visual apparatus, muscle spasms, the inability to control the muscles, and impaired coordination of movements. In severe cases, there may be incoherent speech, a meaningless look, hallucinations, loss of consciousness.
Such manifestations are characteristic of intoxication with plant or animal natural toxins that have a pronounced neurological effect.
Some severe food poisonings show signs of allergic reactions: skin irritation, severe itching, and excessive swelling. Serious intoxications affect the functioning of the liver.
Sufficiently strong toxins that it cannot neutralize can lead to a decrease or complete loss of liver function. This threatens the patient with death. When the first "liver" symptoms appear, you should seek medical help.
First aid

In any food poisoning situation, immediate care is often crucial. The earlier measures are taken to eliminate intoxication, the more effective the treatment will be. If you become infected with toxoinfection through the use of low-quality food, you should definitely consult a doctor. Most often this occurs as a result of the use of canned food prepared at home.
At the first manifestations of food intoxication, residual toxins that have not been absorbed into the blood should be eliminated from the digestive tract.
To do this, you need to do a gastric lavage. For this purpose, the poisoned person is given to drink a large amount of salted water or a weak solution of potassium permanganate. Vomiting should occur until clear water is expelled from the stomach.
To prevent dehydration, it is necessary to maintain water balance. After each vomiting and diarrhea, it is necessary to replenish the losses by drinking a glass of water. It is also recommended to take special products, for example, Regidron powder, water-salt solutions prepared independently. This helps not only prevent dehydration, but also restore electrolyte balance.
After the poisoned person stops vomiting, it is necessary to take measures to eliminate the poisons that have passed through the gastrointestinal tract further.
For this, sorbents are used, the most commonly used of which is activated carbon. Sorbent substances act like a sponge, collecting poisons on their way and removing them naturally. Doctors recommend drinking in this capacity drugs such as Polysorb, Smecta, Enterosgel.
If the symptoms of intoxication do not go away for a long time or the person is in a serious condition, you should immediately consult a doctor. It is best to do this even with mild poisoning, as even these can have serious consequences.
If among the poisoned there are children, elderly people or pregnant women, then a visit to the doctor is mandatory. It is also necessary when blood impurities are observed in vomiting or the contents of the toilet, a person has a critical temperature for a long time, there is fever, confusion, signs of brain damage.
Prevention

Food poisoning prevention measures include:
- buying products only at trusted outlets, refusing to purchase goods "from hand", especially home preservation;
- careful choice of products: checking expiration dates, integrity, tightness of packaging, organoleptic properties (color, smell, consistency);
- thorough washing of vegetables, herbs, fruits before use;
- sufficient heat treatment, especially meat and fish products;
- defrosting food only in the refrigerator (not at room temperature) and immediately before cooking;
- compliance with the conditions for storing cooked food at home;
- compliance with sanitary standards: thorough washing of cutting boards, knives, dishes using disinfectants;
- fight against pathogens and carriers of infectious diseases, persecution of rats, cockroaches, ants, keeping the house clean.

