The surface area of \u200b\u200bthe pyramid. In this article we will consider problems with the correct pyramids. Let me remind you that a regular pyramid is a pyramid whose base is a regular polygon, the top of the pyramid is projected into the center of this polygon.
The side face of such a pyramid is an isosceles triangle.The height of this triangle, drawn from the top of the regular pyramid, is called the apothem, SF - the apothem:

In the type of tasks presented below, it is required to find the surface area of \u200b\u200bthe entire pyramid or the area of \u200b\u200bits lateral surface. The blog has already considered several problems with regular pyramids, where the question was raised about finding elements (height, base edge, side edge),.
In the USE assignments, as a rule, regular triangular, quadrangular and hexagonal pyramids are considered. I did not meet problems with regular pentagonal and heptagonal pyramids.
The formula for the area of \u200b\u200bthe entire surface is simple - you need to find the sum of the area of \u200b\u200bthe base of the pyramid and the area of \u200b\u200bits lateral surface:
![]()
Consider the tasks:
The sides of the base of the regular quadrangular pyramid are 72, the side edges are 164. Find the surface area of \u200b\u200bthis pyramid.

The surface area of \u200b\u200bthe pyramid is equal to the sum of the areas of the side surface and the base:
* The lateral surface consists of four equal in area triangles. The base of the pyramid is a square.
The area of \u200b\u200bthe side of the pyramid can be calculated using:
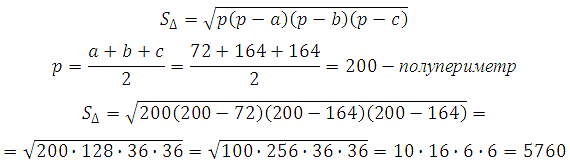
Thus, the surface area of \u200b\u200bthe pyramid is equal to:
Answer: 28224
The sides of the base of the regular hexagonal pyramid are 22, the side edges are 61. Find the area of \u200b\u200bthe side surface of this pyramid.

The base of a regular hexagonal pyramid is a regular hexagon.
The area of \u200b\u200bthe side surface of this pyramid consists of six areas of equal triangles with sides 61.61 and 22:
Find the area of \u200b\u200bthe triangle, use the Heron formula:

Thus, the side surface area is equal to:
![]()
Answer: 3240
* In the above problems, the area of \u200b\u200bthe side face could be found using a different triangle formula, but for this you need to calculate the apothem.
27155. Find the surface area of \u200b\u200bthe regular quadrangular pyramid, the sides of the base of which are 6 and the height is 4.

In order to find the surface area of \u200b\u200bthe pyramid, we need to know the area of \u200b\u200bthe base and the area of \u200b\u200bthe side surface:
The area of \u200b\u200bthe base is 36, since it is a square with side 6.
The side surface consists of four faces, which are equal triangles. In order to find the area of \u200b\u200bsuch a triangle, you need to know its base and height (apothem):
* The area of \u200b\u200bthe triangle is equal to half the product of the base and the height drawn to this base.
The base is known, it is equal to six. Find the height. Consider a right triangle (it is highlighted in yellow):

One leg is 4, since this is the height of the pyramid, the other is 3, since it is equal to half the edge of the base. We can find the hypotenuse, according to the Pythagorean theorem:
![]()
So the area of \u200b\u200bthe side surface of the pyramid is equal to:

Thus, the surface area of \u200b\u200bthe entire pyramid is equal to:
Answer: 96
27069. The sides of the base of a regular quadrangular pyramid are 10, the side edges are 13. Find the surface area of \u200b\u200bthis pyramid.
27070. The sides of the base of a regular hexagonal pyramid are 10, the side ribs are 13. Find the area of \u200b\u200bthe side surface of this pyramid.
There are also formulas for the lateral surface area of \u200b\u200ba regular pyramid. In a regular pyramid, the base is the orthogonal projection of the side surface, therefore:
P - the perimeter of the base, l - apothem of the pyramid
* This formula is based on the triangle area formula.
If you want to learn more about how these formulas are derived, don’t miss, follow the publication of articles.That's all. Success to you!
Sincerely, Alexander Krutitsky.
P.S: I would be grateful if you talk about the site on social networks.
Briefly about the main thing
Surface Area (2019)
Prism surface area
Is there a general formula? No, generally not. You just need to look for the area of \u200b\u200bthe side faces and summarize them.

The formula can be written for direct prism:
Where is the perimeter of the base.

But still, it’s much easier in each case to add up all the areas than to remember additional formulas. For example, we calculate the full surface of a regular hexagonal prism.

All side faces are rectangles. That means.
This has already been deduced when calculating the volume.
So, we get:
Pyramid surface area

For the pyramid, the general rule also applies:
Now let's calculate the surface area of \u200b\u200bthe most popular pyramids.
The surface area of \u200b\u200ba regular triangular pyramid

Let the side of the base be equal and the side rib equal. Need to find and.
Recall now that
This is the area of \u200b\u200ba regular triangle.
And remember how to look for this area. We use the area formula:

We have a "" - this, and a "" - this too, a.
Now we find.
Using the basic area formula and the Pythagorean theorem, we find
Attention: if you have the correct tetrahedron (i.e.), then the formula is as follows:
The surface area of \u200b\u200ba regular quadrangular pyramid

Let the side of the base be equal and the side rib equal.
At the bottom is a square, and therefore.
It remains to find the area of \u200b\u200bthe side face
The surface area of \u200b\u200ba regular hexagonal pyramid.

Let the side of the base be equal and the side rib.
How to find? The hexagon consists of exactly six identical regular triangles. We have already searched for the area of \u200b\u200ba regular triangle when calculating the surface area of \u200b\u200ba regular triangular pyramid; here we use the found formula.
Well, we’ve already looked for the area of \u200b\u200bthe side face twice
Well, the topic is over. If you read these lines, then you are very cool.
Because only 5% of people are able to master something on their own. And if you read to the end, then you got into these 5%!
Now the most important thing.
You figured out a theory on this topic. And again, this ... it's just super! You are already better than the vast majority of your peers.
The problem is that this may not be enough ...
For what?
For the successful passing of the exam, for admission to the institute on the budget and, MOST IMPORTANT, for life.
I will not convince you of anything, just say one thing ...
People who receive a good education earn much more than those who did not. This is statistics.
But this is not the main thing.
The main thing is that they are MORE HAPPY (there are such studies). Perhaps because they are opening up much more opportunities and life becomes brighter? I do not know...
But, think for yourself ...
What is needed to be surely better than others in the USE and ultimately to be ... happier?
BEAT YOUR HAND, SOLVING PROBLEMS ON THIS TOPIC.
On the exam you will not be asked for a theory.
You will need solve problems on time.
And, if you didn’t solve them (MUCH!), You’ll be sure to make a stupid mistake somewhere or just don’t have time.
It's like in sports - you need to repeat many times to win for sure.
Find where you want the collection, necessarily with solutions, detailed analysis and decide, decide, decide!
You can use our tasks (not necessary) and we certainly recommend them.
In order to fill your hand with the help of our tasks, you need to help extend the life of the YouClever textbook that you are reading now.
How? There are two options:
- Unlock all hidden tasks in this article - 299 rub
- Open access to all hidden tasks in all 99 articles of the textbook - 999 rub
Yes, we have 99 such articles in the textbook and you can immediately open access to all tasks and all hidden texts in them.
In the second case we will give you simulator "6000 tasks with solutions and answers, for each topic, for all levels of difficulty." It will definitely be enough to fill your hand in solving problems on any topic.
In fact, this is much more than just a simulator - a whole training program. If necessary, you can also use it for FREE.
Access to all texts and programs is provided at ALL times the site exists.
In conclusion...
If you don’t like our tasks, find others. Just don’t stop at the theory.
“Understood” and “I Can Decide” are completely different skills. You need both.
Find tasks and solve!
In this tutorial:
- Task 1. Find the total surface area of \u200b\u200bthe pyramid.
- Problem 2. Find the lateral surface area of \u200b\u200ba regular triangular pyramid
.
Note . If you need to solve a problem in geometry, which is not here, write about it in the forum. In tasks, instead of the square root symbol, the sqrt () function is used, in which sqrt is the square root symbol, and a radical expression is indicated in brackets. For simple root expressions, the √ sign can be used..
Task 1. Find the total surface area of \u200b\u200ba regular pyramid
The height of the base of the regular triangular pyramid is 3 cm. And the angle between the side face and the base of the pyramid is 45 degrees.Find the total surface area of \u200b\u200bthe pyramid
Decision.
At the base of a regular triangular pyramid lies an equilateral triangle.
Therefore, to solve the problem, we use the properties of a regular triangle: 
We know the height of the triangle, where you can find its area.
h \u003d √3 / 2 a
a \u003d h / (√3 / 2)
a \u003d 3 / (√3 / 2)
a \u003d 6 / √3
From where the base area will be equal to:
S \u003d √3 / 4 a 2
S \u003d √3 / 4 (6 / √3) 2
S \u003d 3√3
In order to find the area of \u200b\u200bthe side face, we calculate the height KM. The OKM angle according to the condition of the problem is 45 degrees.
In this way:
OK / MK \u003d cos 45
Take advantage a table of values \u200b\u200bof trigonometric functions and substitute the known values.
OK / MK \u003d √2 / 2
We take into account that OK is equal to the radius of the inscribed circle. Then
OK \u003d √3 / 6 a
OK \u003d √3 / 6 * 6 / √3 \u003d 1
Then
OK / MK \u003d √2 / 2
1 / MK \u003d √2 / 2
MK \u003d 2 / √2
The area of \u200b\u200bthe lateral face is then equal to half the product of height by the base of the triangle.
S side \u003d 1/2 (6 / √3) (2 / √2) \u003d 6 / √6
Thus, the total surface area of \u200b\u200bthe pyramid will be equal to
S \u003d 3√3 + 3 * 6 / √6
S \u003d 3√3 + 18 / √6
Answer: 3√3 + 18/√6
Task 2. Find the lateral surface area of \u200b\u200ba regular pyramid
In a regular triangular pyramid, the height is 10 cm, and the side of the base is 16 cm . Find the lateral surface area .Decision.
Since the base of a regular triangular pyramid is an equilateral triangle, AO is the radius of the circle circumscribed around the base.
(It follows from)
The radius of the circle circumscribed around an equilateral triangle will be found from its properties 
From where the length of the edges of the regular triangular pyramid will be equal to:
AM 2 \u003d MO 2 + AO 2
the height of the pyramid is known by the condition (10 cm), AO \u003d 16√3 / 3
AM 2 \u003d 100 + 256/3
AM \u003d √ (556/3)
Each side of the pyramid is an isosceles triangle. The area of \u200b\u200bthe isosceles triangle will be found from the first formula below 
S \u003d 1/2 * 16 sqrt ((√ (556/3) + 8) (√ (556/3) - 8))
S \u003d 8 sqrt ((556/3) - 64)
S \u003d 8 sqrt (364/3)
S \u003d 16 sqrt (91/3)
Since all three faces of the regular pyramid are equal, the area of \u200b\u200bthe side surface will be equal
3S \u003d 48 √ (91/3)
Answer: 48 √(91/3)
Problem 3. Find the total surface area of \u200b\u200bthe regular pyramid
The side of the regular triangular pyramid is 3 cm and the angle between the side face and the base of the pyramid is 45 degrees. Find the area of \u200b\u200bthe full surface of the pyramid.
Decision.
Since the pyramid is correct, an equilateral triangle lies at its base. Therefore, the base area is 
So \u003d 9 * √3 / 4
In order to find the area of \u200b\u200bthe side face, we calculate the height KM. The OKM angle according to the condition of the problem is 45 degrees.
In this way:
OK / MK \u003d cos 45
Take advantage
In preparing for the exam in mathematics, students have to systematize knowledge of algebra and geometry. I would like to combine all the known information, for example, on how to calculate the area of \u200b\u200bthe pyramid. And starting from the base and side faces to the area of \u200b\u200bthe entire surface. If the situation with the side faces is clear, since they are triangles, then the base is always different.
What to do when finding the area of \u200b\u200bthe base of the pyramid?
It can be absolutely any figure: from an arbitrary triangle to an n-gon. And this basis, in addition to the difference in the number of angles, can be the right figure or the wrong one. In tasks of interest to students on the exam, there are only tasks with the correct figures at the base. Therefore, we will only talk about them.
Right triangle
That is equilateral. One in which all sides are equal and are marked with the letter “a”. In this case, the base area of \u200b\u200bthe pyramid is calculated by the formula:
S \u003d (a 2 * √3) / 4.
Square
The formula for calculating its area is the simplest, here “a” is again the side:
Arbitrary regular n-gon
The side of the polygon has the same notation. The latin letter n is used for the number of angles.
S \u003d (n * a 2) / (4 * tg (180º / n)).

What to do when calculating the area of \u200b\u200bthe lateral and full surface?
Since the base is the correct figure, then all the faces of the pyramid are equal. Moreover, each of them is an isosceles triangle, since the side ribs are equal. Then, in order to calculate the lateral area of \u200b\u200bthe pyramid, you need a formula consisting of the sum of identical monomials. The number of terms is determined by the number of sides of the base.
The area of \u200b\u200ban isosceles triangle is calculated by the formula in which half the product of the base is multiplied by the height. This height in the pyramid is called the apothem. Its designation is “A”. The general formula for the lateral surface area is as follows:
S \u003d ½ P * A, where P is the perimeter of the base of the pyramid.
There are situations when the sides of the base are not known, but side ribs (c) and a flat angle at its apex (α) are given. Then it is supposed to use such a formula to calculate the lateral area of \u200b\u200bthe pyramid:
S \u003d n / 2 * in 2 sin α .

Task number 1
Condition. Find the total area of \u200b\u200bthe pyramid, if at its base lies with a side of 4 cm, and the apothem has a value of √3 cm.
Decision. It must begin with the calculation of the perimeter of the base. Since this is a regular triangle, P \u003d 3 * 4 \u003d 12 cm. Since the apothem is known, we can immediately calculate the area of \u200b\u200bthe entire lateral surface: ½ * 12 * √3 \u003d 6√3 cm 2.
For the triangle at the base, this is the area value: (4 2 * √3) / 4 \u003d 4√3 cm 2.
To determine the entire area, you need to add two resulting values: 6√3 + 4√3 \u003d 10√3 cm 2.
Answer. 10√3 cm 2.
Task number 2
Condition. There is a regular quadrangular pyramid. The length of the side of the base is 7 mm, the side rib is 16 mm. It is necessary to find out its surface area.
Decision. Since the polyhedron is quadrangular and regular, then at its base lies a square. Having learned the area of \u200b\u200bthe base and the side faces, it will be possible to calculate the area of \u200b\u200bthe pyramid. The formula for the square is given above. And at the side faces, all sides of the triangle are known. Therefore, you can use the Heron formula to calculate their area.
The first calculations are simple and lead to such a number: 49 mm 2. For the second value, you need to calculate the half-perimeter: (7 + 16 * 2): 2 \u003d 19.5 mm. Now you can calculate the area of \u200b\u200ban isosceles triangle: √ (19.5 * (19.5-7) * (19.5-16) 2) \u003d √2985.9375 \u003d 54.644 mm 2. There are only four such triangles, so when calculating the final number, you will need to multiply it by 4.
It turns out: 49 + 4 * 54.644 \u003d 267.576 mm 2.
Answer. The desired value is 267.576 mm 2.
Task number 3
Condition. The correct quadrangular pyramid needs to calculate the area. The side of the square is known in it - 6 cm and height - 4 cm.
Decision. The easiest way to use the formula with the product of the perimeter and apothem. The first value is easy to find. The second is a bit more complicated.
We will have to recall the Pythagorean theorem and consider it. It is formed by the height of the pyramid and apothem, which is a hypotenuse. The second leg is equal to half the side of the square, since the height of the polyhedron falls in its middle.
The desired apothem (hypotenuse of a right triangle) is √ (3 2 + 4 2) \u003d 5 (cm).
Now you can calculate the desired value: ½ * (4 * 6) * 5 + 6 2 \u003d 96 (cm 2).
Answer. 96 cm 2.

Task number 4
Condition. The correct one is given. The sides of its base are 22 mm, the side ribs are 61 mm. What is the lateral surface area of \u200b\u200bthis polyhedron?
Decision. The reasoning in it is the same as was described in task No. 2. Only there was given a pyramid with a square at the base, and now it is a hexagon.
First of all, the base area is calculated according to the above formula: (6 * 22 2) / (4 * tg (180º / 6)) \u003d 726 / (tg30º) \u003d 726√3 cm 2.
Now you need to find out the half-perimeter of an isosceles triangle, which is a side face. (22 + 61 * 2): 2 \u003d 72 cm. It remains to use Heron’s formula to calculate the area of \u200b\u200beach such triangle, and then multiply it by six and add it to the one obtained for the base.
Calculations according to the Heron formula: √ (72 * (72-22) * (72-61) 2) \u003d √435600 \u003d 660 cm 2. Calculations that give the area of \u200b\u200bthe lateral surface: 660 * 6 \u003d 3960 cm 2. It remains to fold them to find out the entire surface: 5217.47≈5217 cm 2.
Answer. The bases are 726√3 cm 2, the lateral surface is 3960 cm 2, the entire area is 5217 cm 2.

